Non Mobile Echogenic Foci Gallbladder
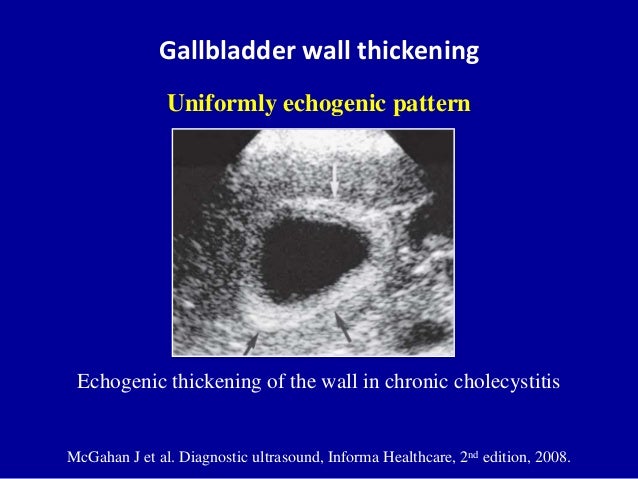
The comet tail artefacts are the result of minute cholesterol calculi within small sinuses or diverticuli (Rokitansky -Aschoff sinuses) in the Gall bladder wall.
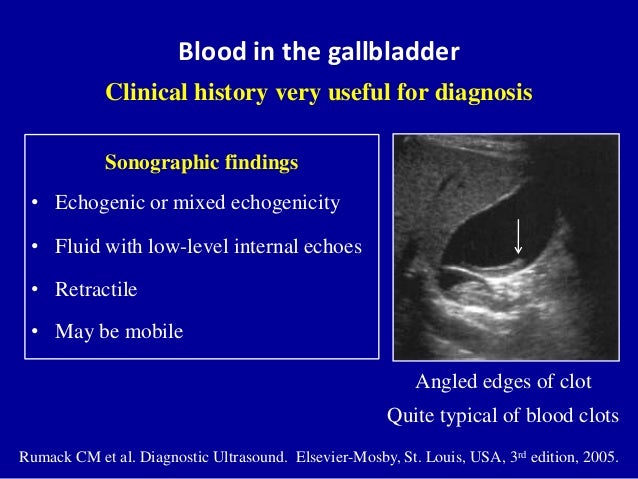
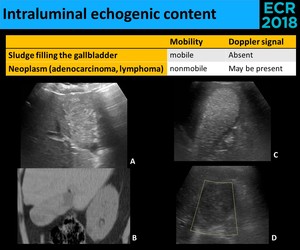
Non mobile echogenic foci gallbladder. The mobility of an intraluminal focus is a sign that is useful in equivocal cases (i.e., where a definite acoustic shadow is not demonstrated). Wat is the treatment for this?. Dec 23, 18 - Dedicated to the mission of bringing free or low-cost educational materials and information to the global ultrasound community.
Diseases of the Gall Bladder • Cholelithiasis • Porcelain GB • Mirrizzi Syndrome. Few mobile calculi are seen, largest measuring 6.2 mm. Whether all echogenic foci in the fetal gallbladder represent true gallstones remains unknown.
No gross focal mass is seen within pancreatic body and portions of pancreatic head. 445 Disorders of the biliary tract with cc;. 444 Disorders of the biliary tract with mcc;.
Finally, there is a highly echogenic line of superficial stones with associated posterior shad-owing. Hi, So i had another ultrasound done to check for gallstones and they found 2 this time "up to 7mm, non mobile echogenic foci" and it was said they cld be "wall adherent soft stones or gallbladder pol … read more. This likely represents a gallbladder polyp.
An echogenic focus poses no health risk to the fetus, and when it is born, there are no risks to the baby’s health or cardiac functioning. Gallbladder polyps are elevated lesions on the mucosal surface of the gallbladder. Also seen are small gallstones layering dependently with associated distal acoustic shadowing.
Sludge in the Gallbladder. Gallbladder polyps larger than 1/2 inch in diameter are more likely to be cancerous or turn into cancer over time, and those larger than 3/4 inch (almost 2 centimeters) in diameter may pose a significant risk of being malignant. Gallstones appear as echogenic foci in the gallbladder.
Differential Diagnosis of a Gallbladder Mass Seen at US. No evidence of a calcified stone within the gallbladder or the visualized biliary tree. (Gall bladder is normal in contours.
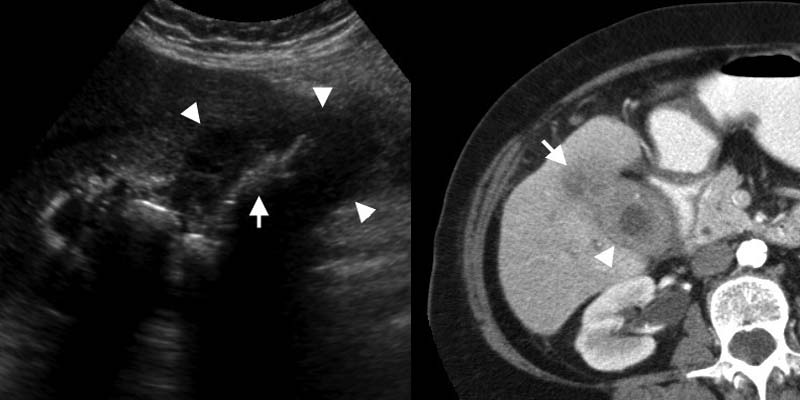
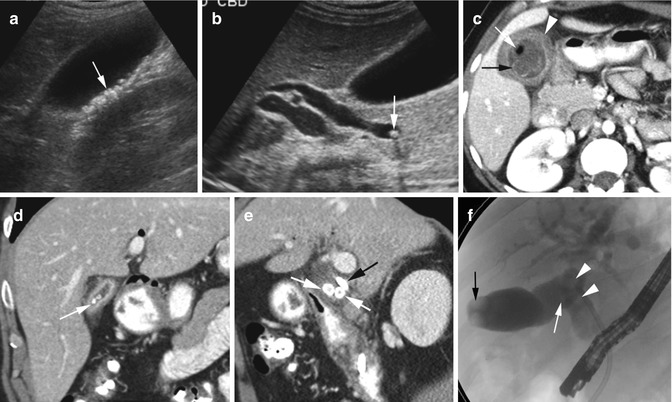
A noncalcified filling defect is present in the gallbladder on this contrast-enhanced CT. Echogenic foci typically represent gallstones versus the much less common porcelain gallbladder (Fig. These echoes do not cast an acoustic shadow.
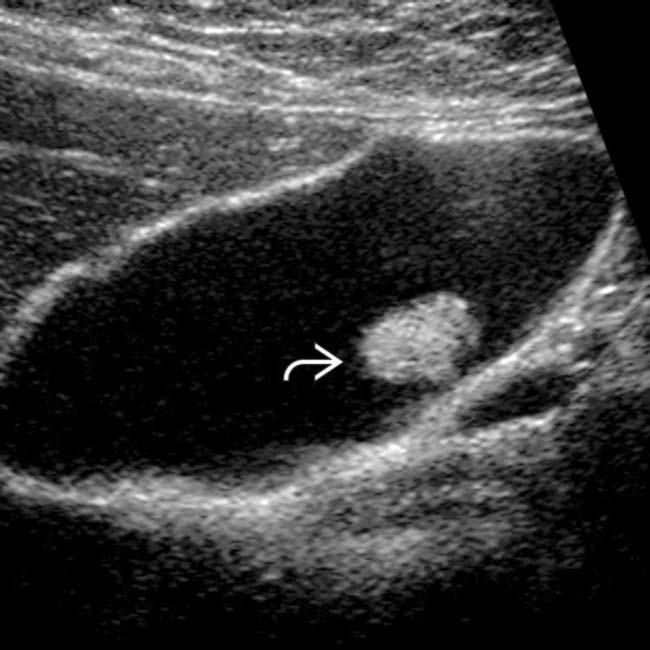
The mass is occasionally adherent (ie, nonmobile) Cholesterol polyp:. Echogenic focus in the gallbladder lumen. Echogenic foci in the gallbladder are usually small polyps.
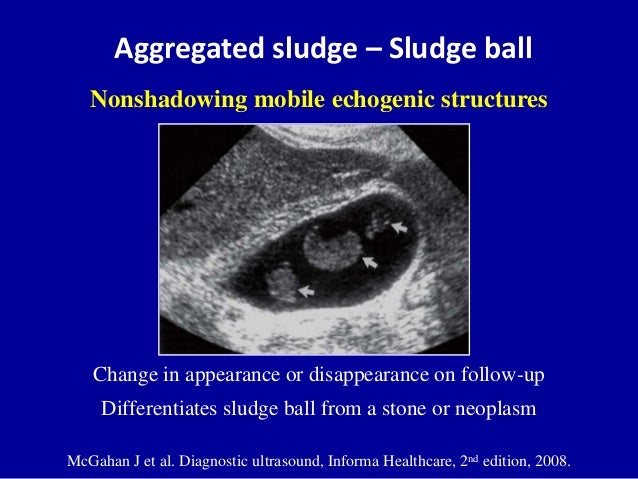
It is sometimes called biliary sludge because it occurs when bile stays. On imaging, although they may be detected by CT or MRI, they are usually best characterized on ultrasound as a non-shadowing and immobile polypoid ingrowth into gallbladder lumen. Gallbladder is partially distended, showing two echogenic foci , not casting posterior acoustic shadowing , measuring 3.0 mm." Answered by Dr.
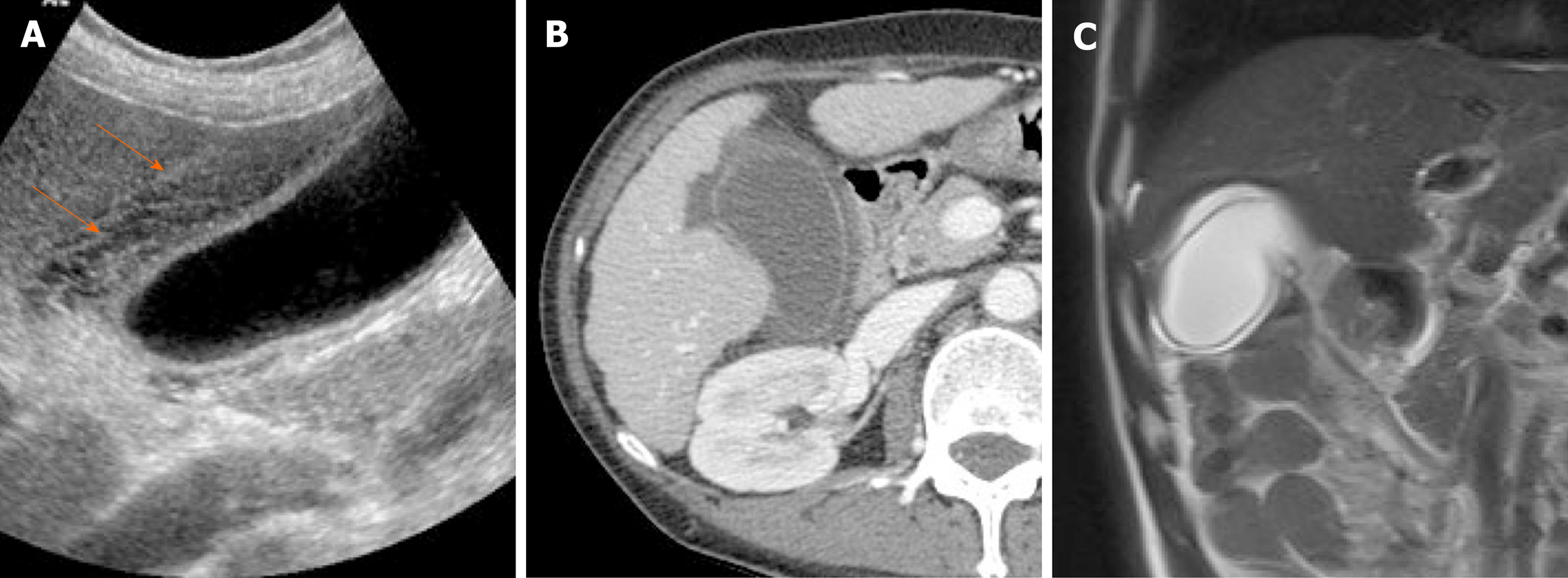
Also not able to eat much without getting sick. There is also diffuse thickening of the gall bladder wall. Within the neck of the gallbladder, there is a calculus which is non-mobile.
I go to see my regular doctor on monday but i have also have had. 43 Both gallstones and porcelain gallbladder arewell described risk factors, although the association between gallbladder carcinoma and porcelain gallbladder may not be as evident as previously thought. Non-mobile, echogenic mass protruding into or filling entire gallbladder lumen in association with cholelithiasis.
Common bile duct is dilated 3mm in diameter. 446 Disorders of the biliary tract without cc/mcc;. Echogenic material in the gallbladder is debris formed in the bile of the gallbladder.
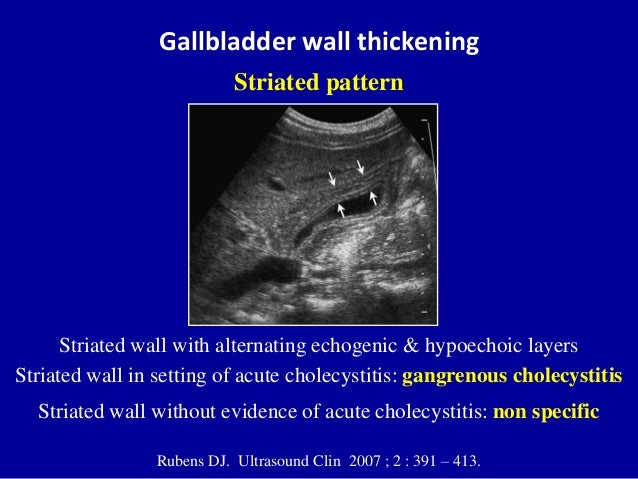
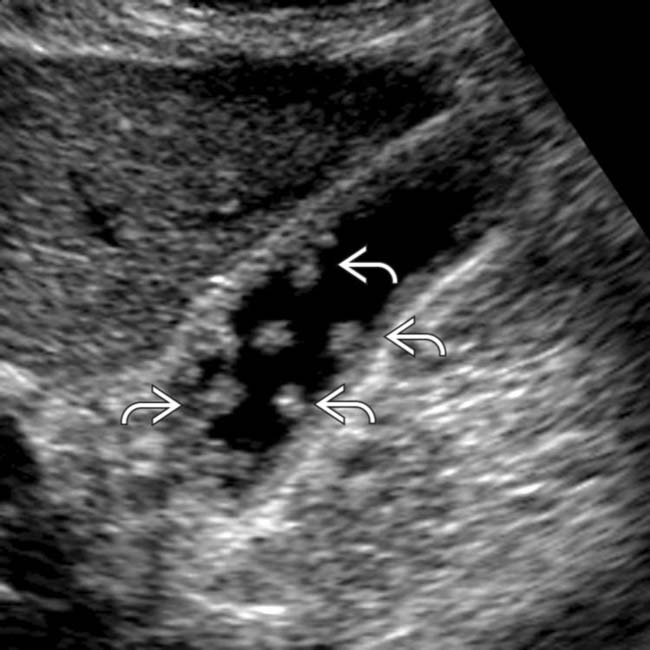
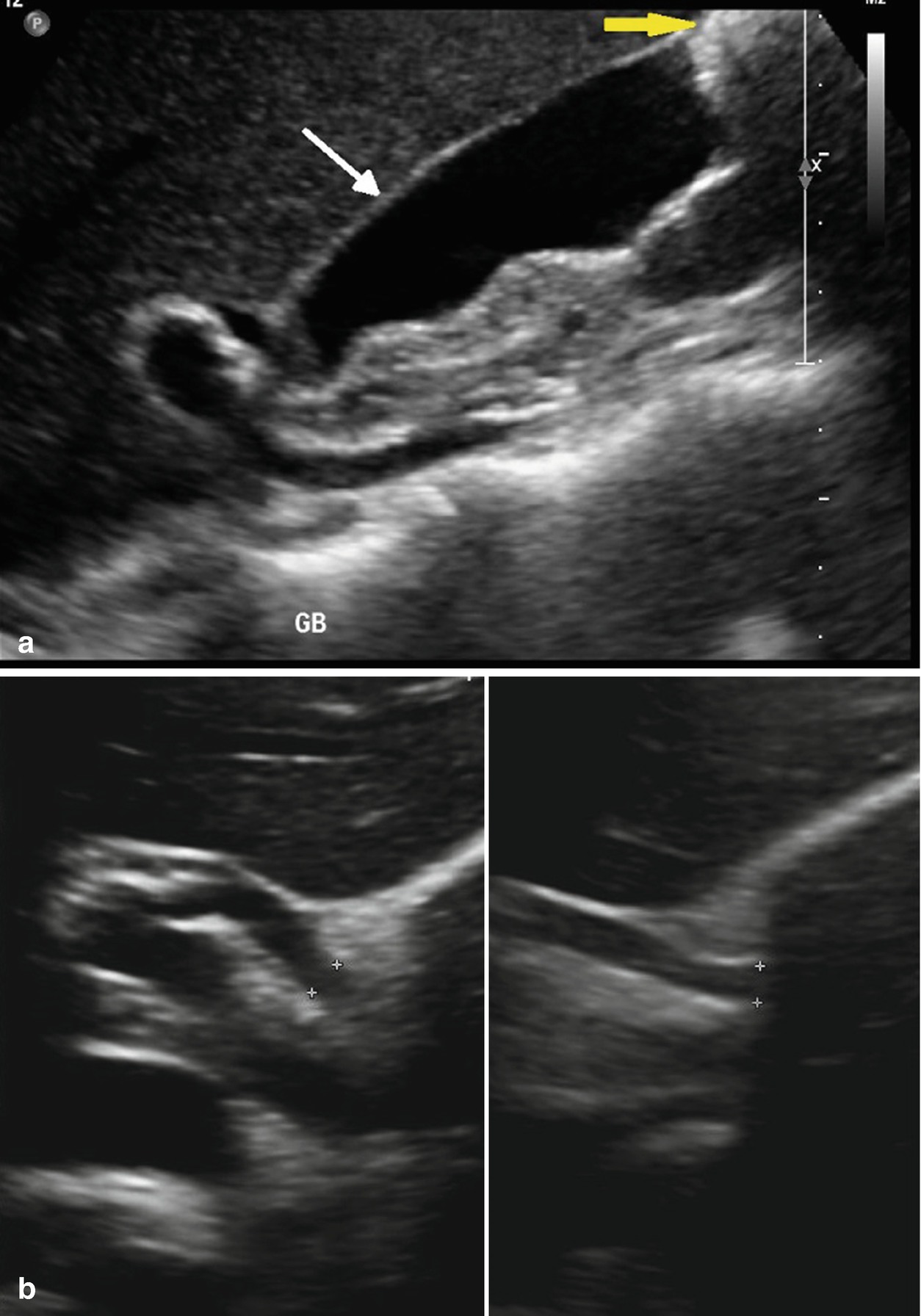
A non-mobile, echogenic focus without posterior acoustic shadowing is seen within the gallbladder with associated thickening of the gallbladder wall. These gall bladder ultrasound images show multiple echogenic foci within the GB wall with V-shaped comet-tail artefacts. Anechoic foci of trapped bile or necrotic tumor may be present, as well as echogenic shadowing foci from gallstones, porcelain gallbladder, or tumor calcifications.
I recently had a gall bladder sonogram - it showed a non-shawdowing 0.4 x 0.6 x 0.7 cm echogenic focus in mid pole which could reflect an atipical stone, small hemorrhagic cyst , vascular calcification. Hi, So i had another ultrasound done to check for gallstones and they found 2 this time "up to 7mm, non mobile echogenic foci" and it was said they cld be "wall adherent soft stones or gallbladder polyps" by the doctor. Ek″o-jen´ik in ultrasonography , giving rise to reflections (echoes) of ultrasound waves.
Although not well understood, we. Therefore, a follow-up ultrasound might be necessary;. Statistically this represents a cholesterol polyp.
Sign (8) (Fig 5). However, in many cases sludge doesn't cause any problems at all. Please consult your primary surgeon also.
Department of Radiological Sciences, University of Santo Tomas Hospital, Manila, Philippines. Echogenic foci may be seen in the fetal gallbladder during the third trimester. I had an ultrasound done.
There is a 0.5 cm nonshadowing echogenic focus along the wall the fundus of the gallbladder that is nonmobile. Non-shadowing echogenic structures within the gallbladder indicates soft to firm structures like polyp or bile sludge rather than stones!. Further echogenic foci which are punctate and show 'comet tail' artefact and are consistent with cholesterolosis.
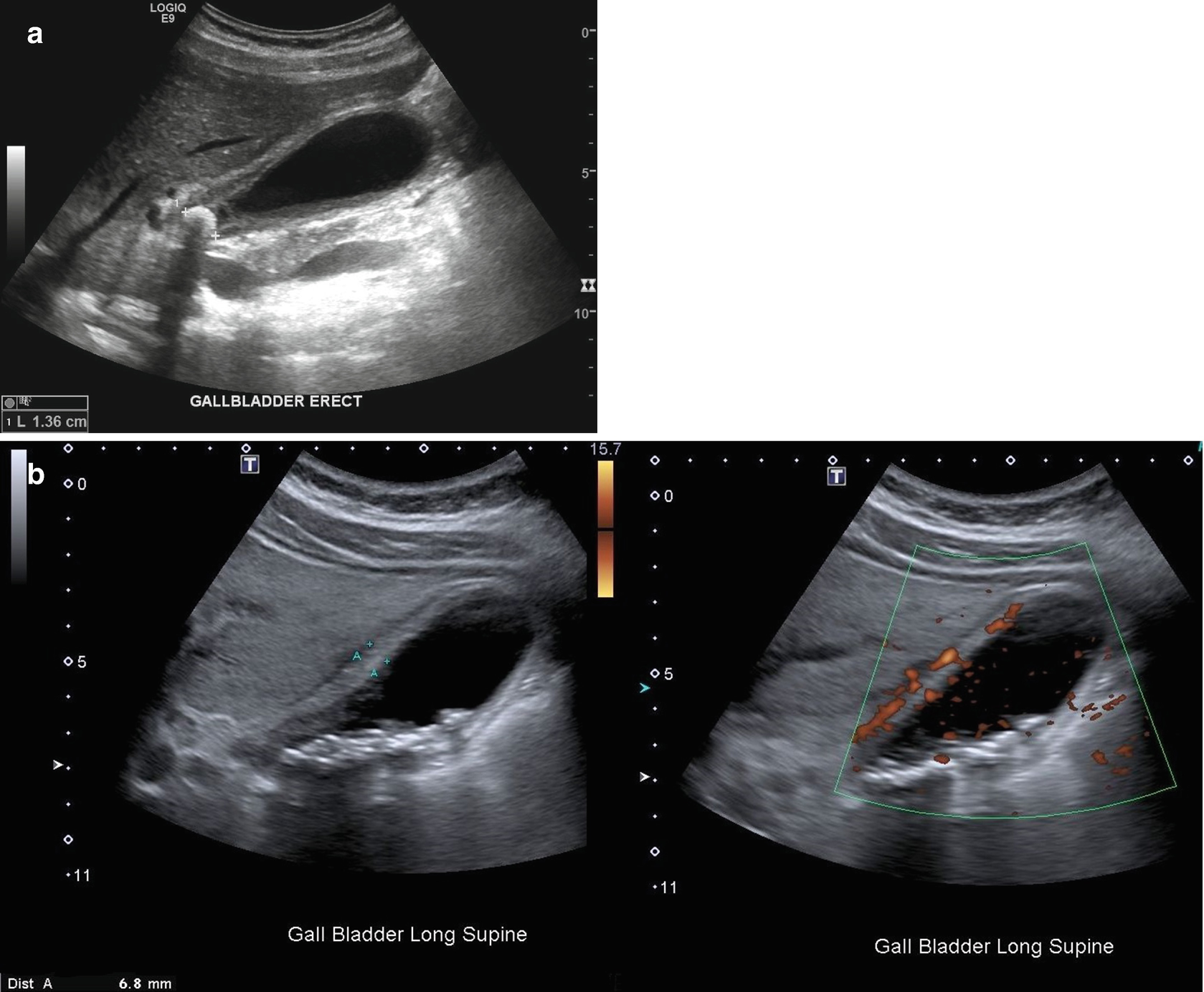
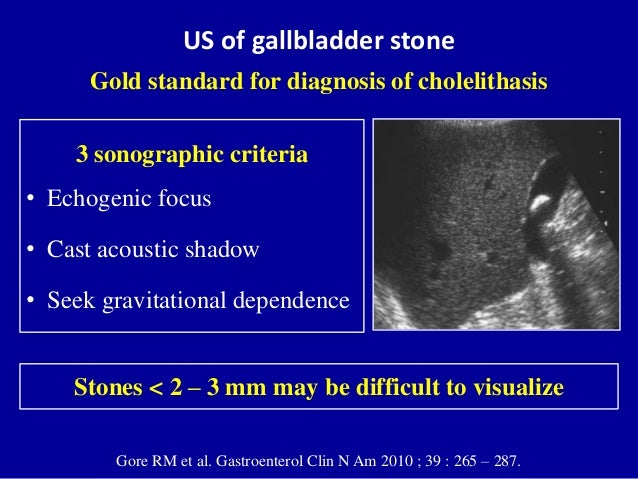
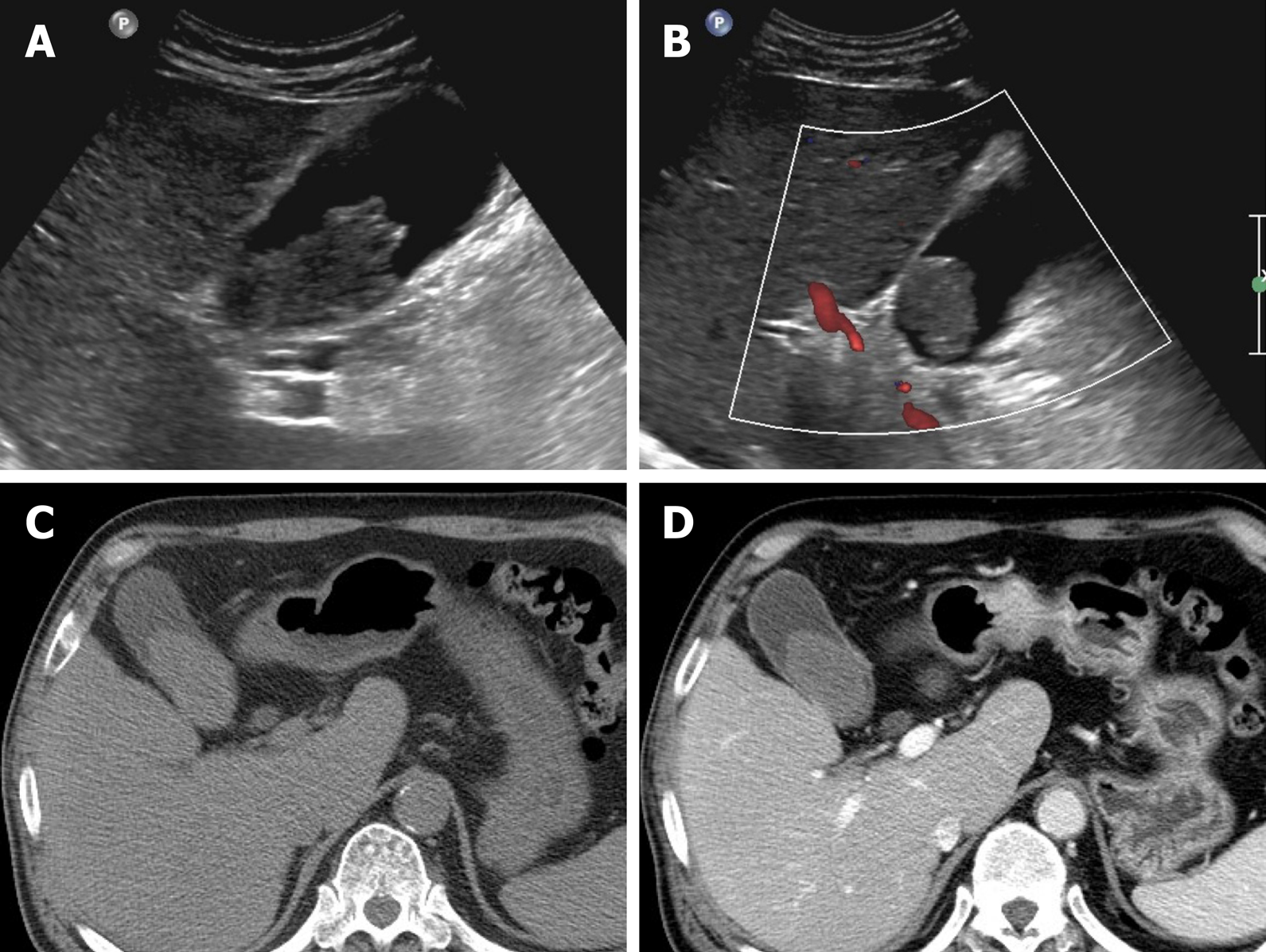
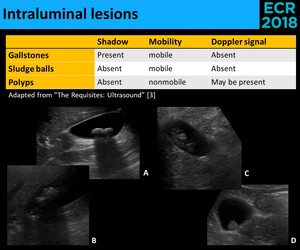
R93-Abnormal findings on diagnostic imaging of other body structures 21 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R93.2. If these are XXXXXXX then the possibility of sludge rather than polyp is more;. On US, nonimpacted gallstones tend to appear as mobile, echogenic foci in a dependent position with “clean” (echo-free) posterior acoustic shadowing (Fig.
THESE FAVOUR SOFT/FIRM BODIES RATHER THAN STONES!. Gallbladder sludge forms when bile remains in the gallbladder for too long. New code (first year of non-draft.
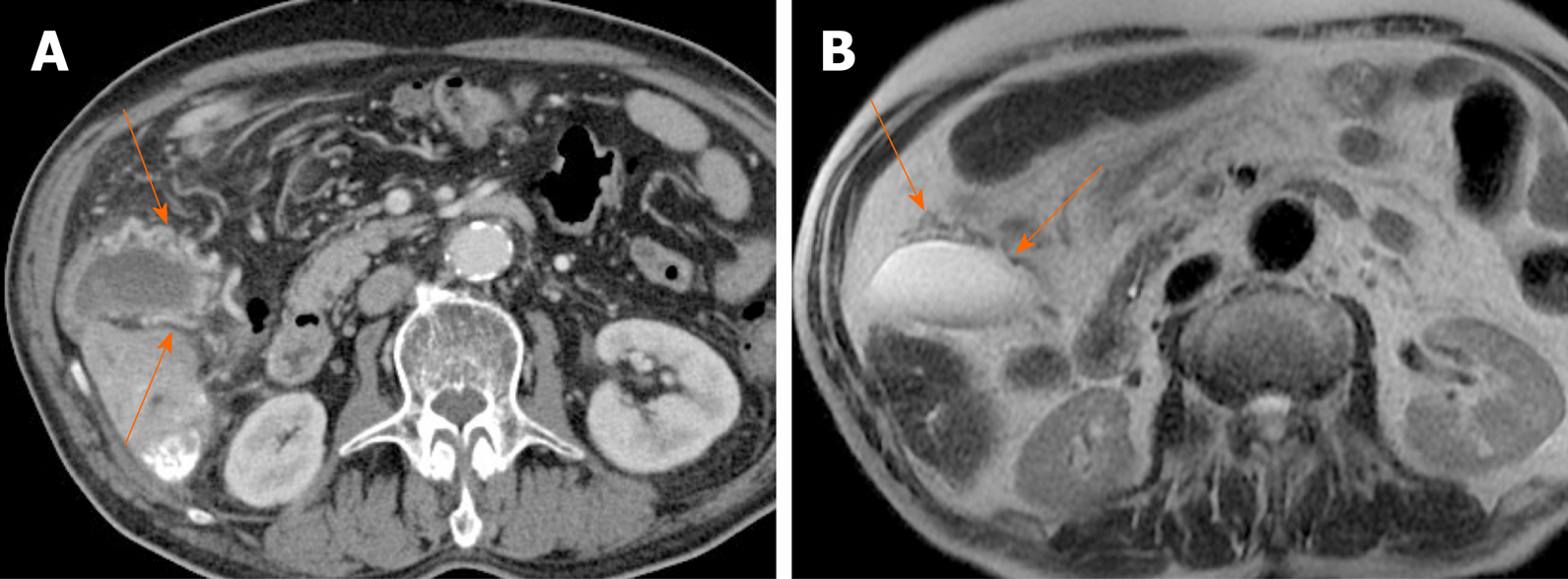
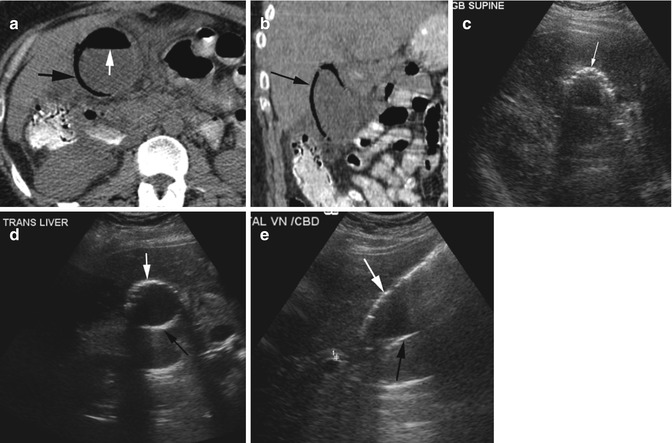
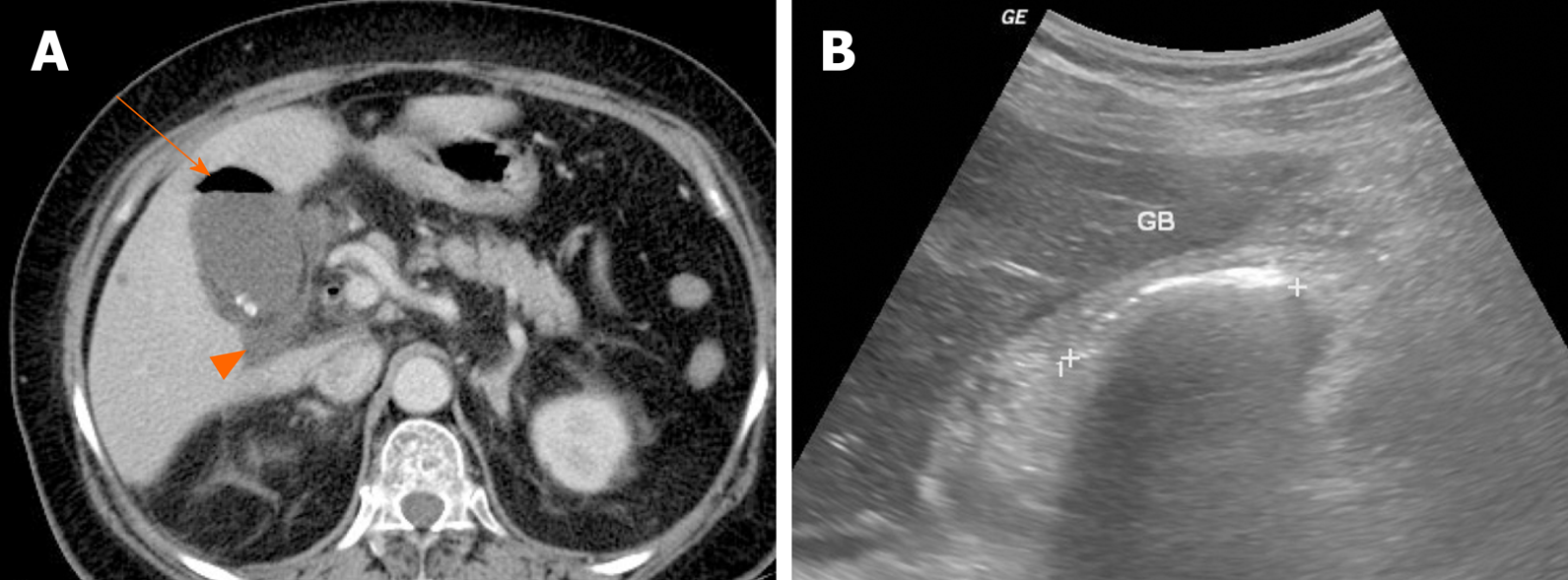
The bright linear echo within the liver connecting the gallbladder and the right portal vein that is the sonographic landmark leading to the gallbladder fossa is the main lobar fissure An extrahepatic mass, such as a carcinoma in the head of the pancreas, compressing the common bile duct can produce an enlarged gallbladder. The common duct measured 0.46 cm. Echogenic mass with shadowing, usually mobile:.
Mucus from the gallbladder can mix with cholesterol and calcium salts, combining to create the sludge. Can this be treated by homeopathy, Lazer for stone breakage or removal of gall bladder?. R90-R94 Abnormal findings on diagnostic imaging and in function studies, without diagnosis ;.
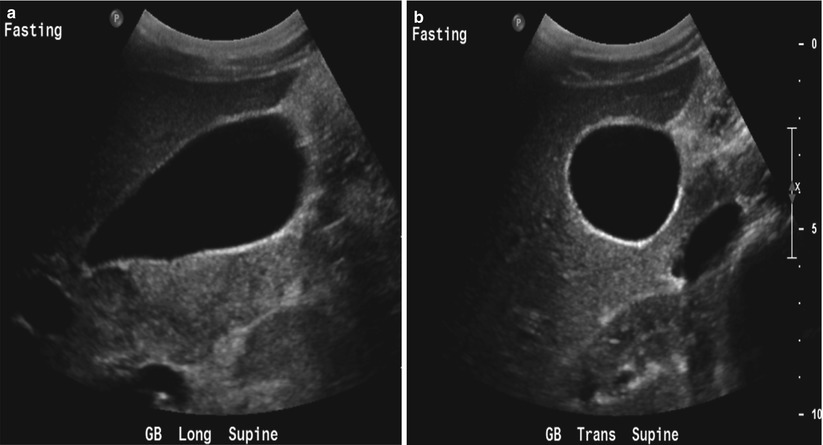
Gall Bladder is well distended. Unfortunately my doctor is away for 2 weeks and only he can answer that. If an EIF is the only notable finding on the ultrasound, it is considered an.
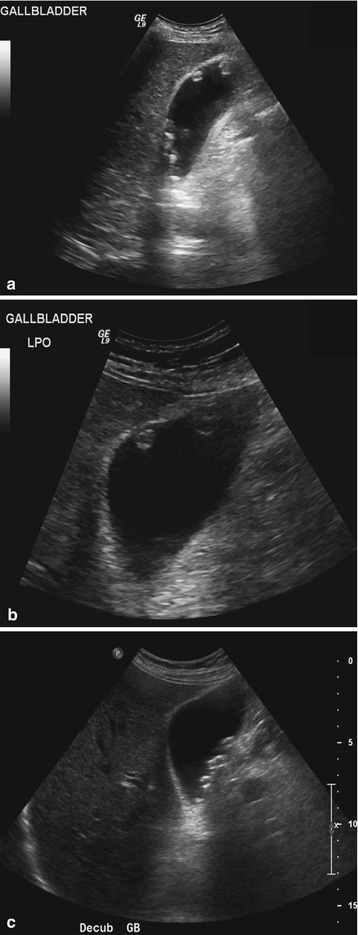
Transverse sonogram of the gallbladder. They move freely with positional changes and cast an acoustic shadow. Hi doctor, 22 yrs, Gall bladder polyp.
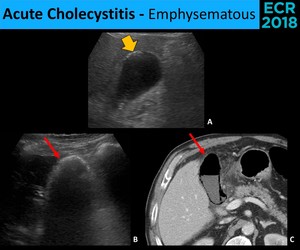
• highly echogenic foci from gas in the intrahepatic biliary tree • weak shadowing. It is considered a variation of normal heart anatomy and is not associated with any short or long-term health problems. (See the image below.) Cholecystitis with small stones in the.
The echogenic foci attached to the gall bladder wall are demonstrated again here and show the classic ‘ring-down’ artifacts that are typical of cholesterol crystals. ICD-10-CM K.8 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v 38.0):. Gallbladder sludge is a collection of cholesterol, calcium, bilirubin, and other compounds that build up in the gallbladder.
I have been having right sided pain for 3 weeks. Convert K.8 to ICD-9-CM. Jul 27, 18 - Dedicated to the mission of bringing free or low-cost educational materials and information to the global ultrasound community.
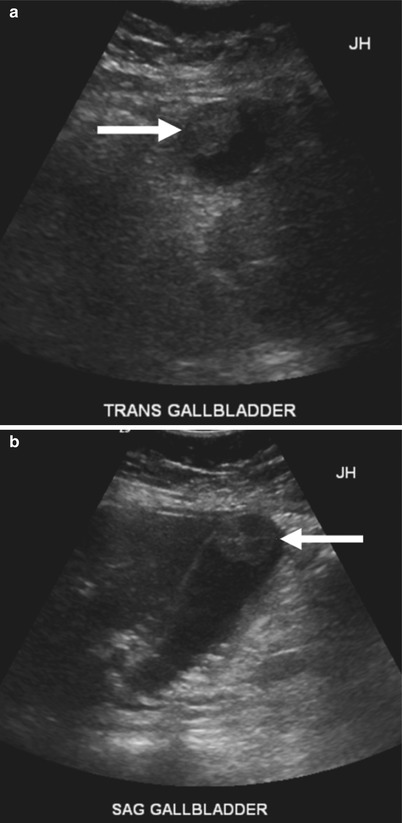
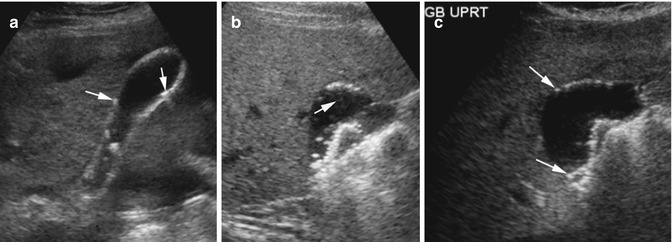
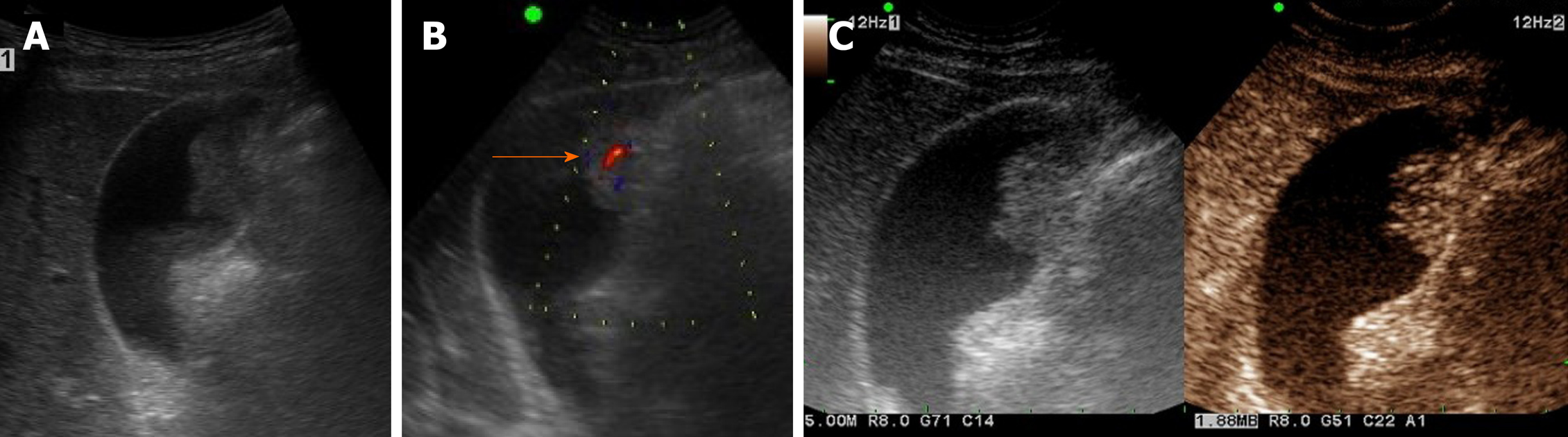
Nonshadowing, nonmobile, echogenic foci attached to the gallbladder wall most likely represent. Hyperechoic foci in the gallbladder wall as a sign of microabscess formation or diverticula Radiology. An adenomatous polyp is less likely however followup is recommended to ensure stability.
A tiny polyp also noted. The vast majority are benign, but malignant forms are seen. In three, the foci have persisted, but none of the children have become symptomatic;.
• non-mobile, non-shadowing echogenic mass protruding into the lumen of the GB. Gall stones cast acoustic shadows , with out as. Shadowing or mobility often differentiates gallstones from polyps.
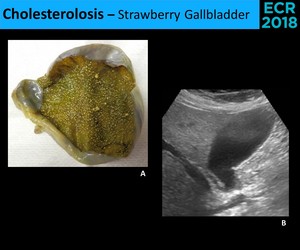
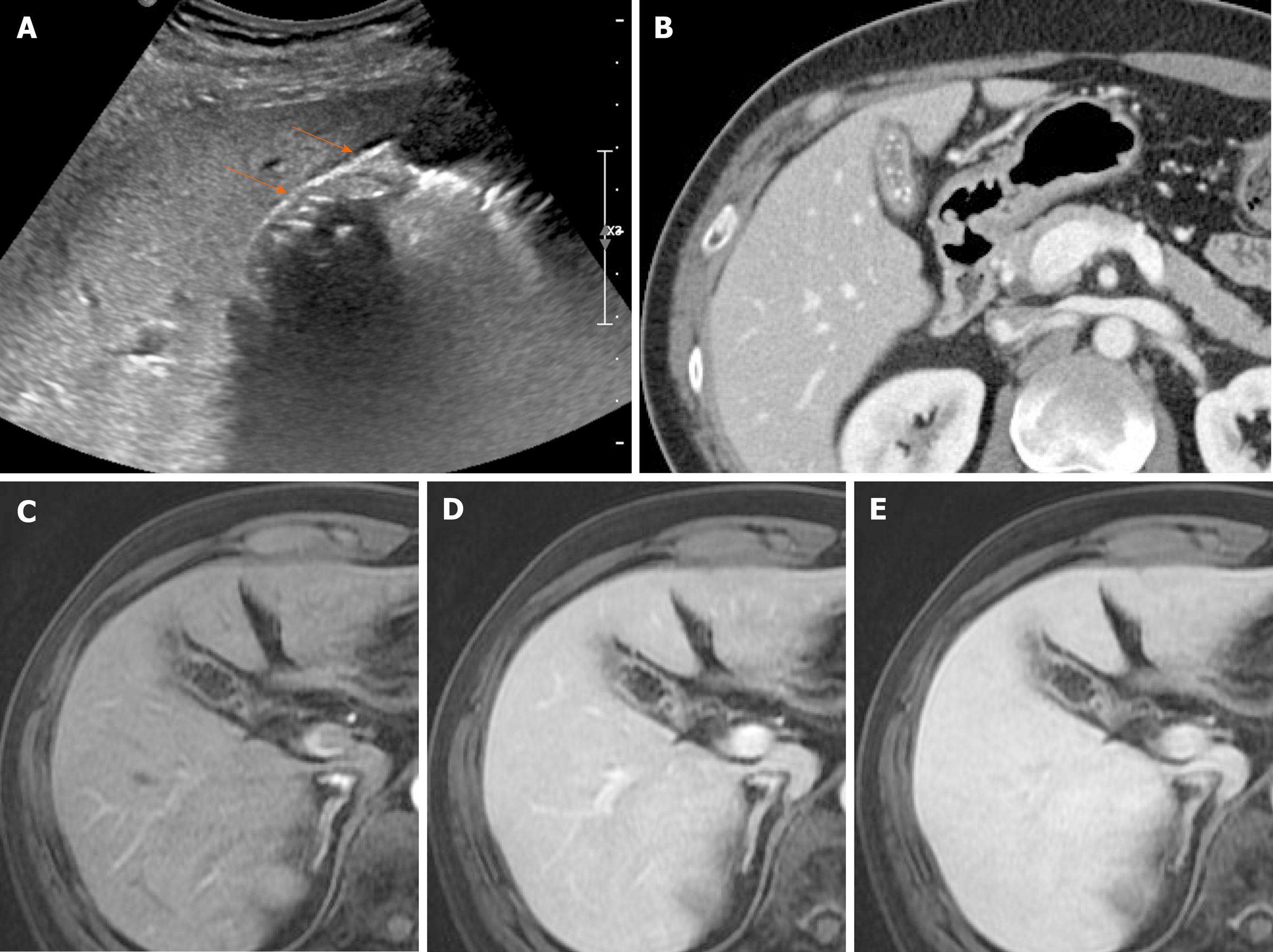
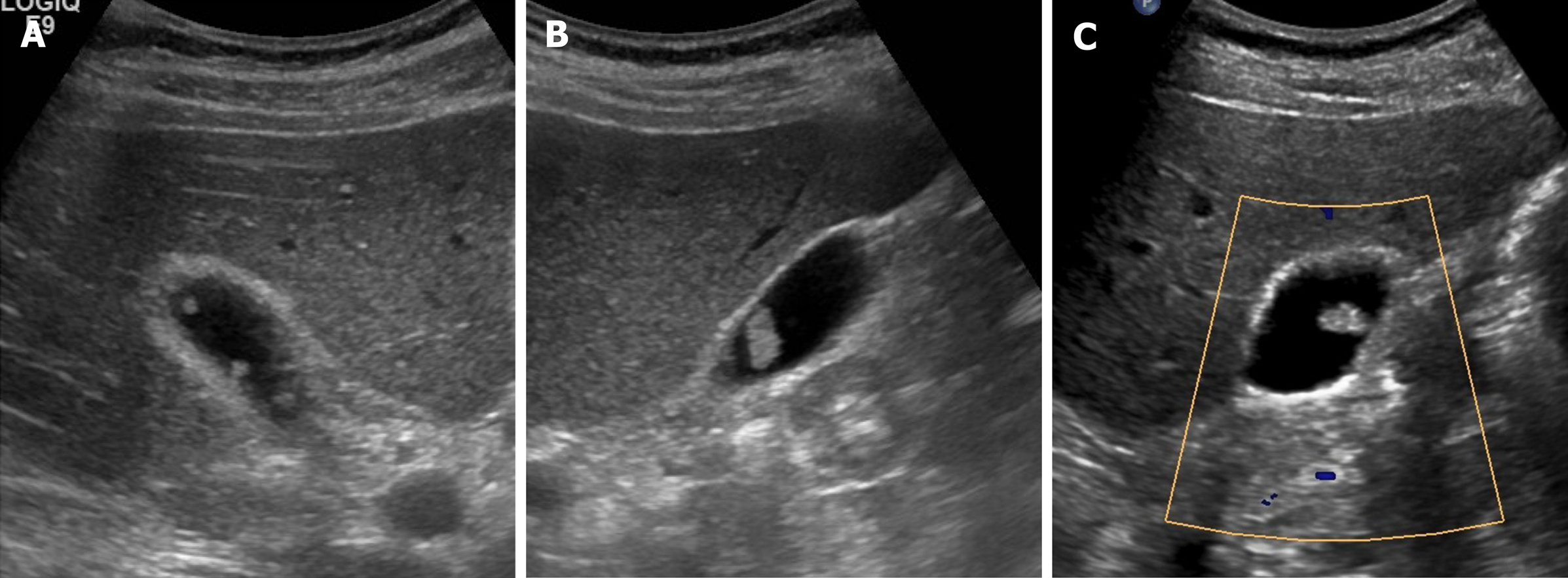
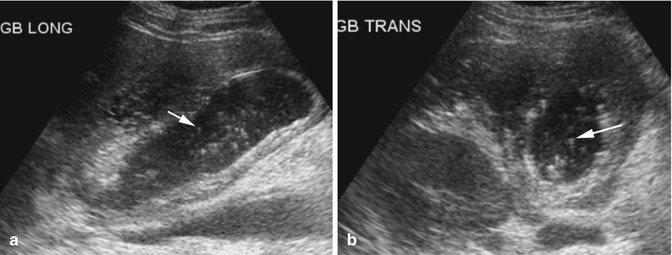
Results were, 6mm left hepatic cyst there are multiple non-mobile hyperechoic foci along the gallbladder wall which do not shadow. Excessive proliferation of surface epithelium/glandular tissue, forms stones that get stuck in the diverticula, non-mobile echogenic foci, comet tail artifact, asymptomatic Gallbladder Polyp - General. Gallbladder wall thickening, echogenic foci withing the gallbladder exhibiting "ring down" Cholesterosis/ "Strawberry GB" (type of hyperplastic cholecystoses).
However i wanted to ask if they are 2 separate stones or growing out of one another. Nal US scan shows two nonshadowing, nonmobile echogenic masses in the gallbladder (arrows), which represent metastatic melanoma. Transverse sonogram of the gallbladder, with the echogenic foci seen to be arising from the gallbladder wall, demonstrating ring down reverberation artifacts.
Treatment of larger gallbladder polyps includes surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy). Also known as gallbladder sludge, it shifts about from time to time within the gallbladder. Cholesterolosis is a condition affecting the gallbladder that happens when cholesteryl esters build up and stick to the wall of the gallbladder, forming polyps.
No gallstones or sludge is noted. Sagittal sonogram of the gallbladder shows multiple, echogenic, non-mobile foci without posterior shadowing, located in the wall. A 5mm immobile echogenic focus noted along the wall of Gall bladder means?.
Primary gallbladder carcinoma is usually hypodense on unenhanced CT, with up to 40% of lesions showing hypervascular foci of enhancement equal to or greater than that of liver. The pain gets very bad in the evenings, where i need something for the pain. Ultrasonography is highly accurate in detecting gallstones and is the preferred imaging modality.
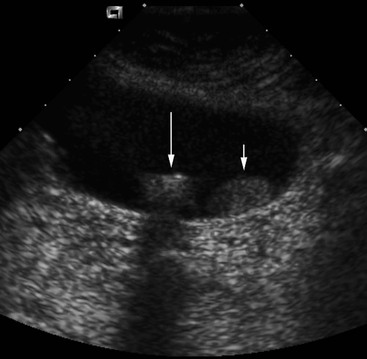
Unifocal form of cholesterolosis:. 1- Echogenic focus in the gallbladder lumen (Picture 1), 2- An acoustic shadow posterior to the echogenic focus (Picture 2). Hi, XXXXXXX XXXXXXX thanks for your query!.
Ultrasound examination confirmed a mobile stone and excluded the other possible diagnoses of polyp or tumor. The longest period of follow-up with stones still present is 4 1/2 years. The material can produce low level echoes, which makes it an echogenic material.
Answer to Nonshadowing, nonmobile, echogenic foci attached to the gallbladder wall most likely represent a. Within some of the cystic spaces, there are echogenic foci some of which demonstrate posterior acoustic shadowing consistent with stones. They can be seen on an ultrasound and are often benign.
Ultrasound - 3mm echogenic non-shadowing, non-mobile foci along gallbladder wall, consistent with a gall bladder polyp. The anterior wall of the gallblad-der is echogenic, below which is a thin, dark line of bile;.
Epos

Ultrasound Of The Gallbladder
An Echogenic Non Mobile Structure Attached To The Gallbladder Wall Download Scientific Diagram
Non Mobile Echogenic Foci Gallbladder のギャラリー
Benign Gallbladder Diseases Imaging Techniques And Tips For Differentiating With Malignant Gallbladder Diseases

Ultrasound Of The Gallbladder
Q Tbn 3aand9gctwugggqdvfsddgmezhblksaegjbbn9txrjbmsonv63vw6ltgpu Usqp Cau

Gallbladder Stones Imaging And Intervention Radiographics
Ultrasound Of The Gallbladder
Benign Gallbladder Diseases Imaging Techniques And Tips For Differentiating With Malignant Gallbladder Diseases
Biliary Imaging For Gallstone Disease Springerlink
Epos

An Echogenic Non Mobile Structure Attached To The Gallbladder Wall Download Scientific Diagram

Gallbladder And Biliary Radiology Key

An Echogenic Non Mobile Structure Attached To The Gallbladder Wall Download Scientific Diagram
Gallbladder Polyps Radiology Key

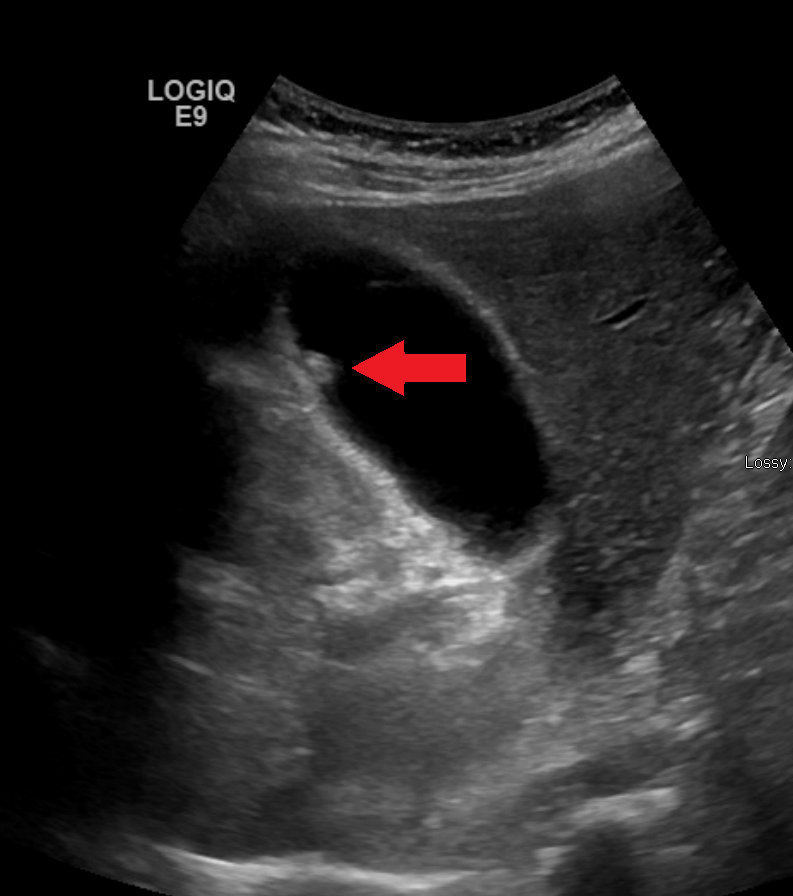
Us Image Of An Immobile Echogenic Focus Arising From The Gallbladder Download Scientific Diagram
The Radiology Assistant Gallbladder Wall Thickening
Benign Gallbladder Diseases Imaging Techniques And Tips For Differentiating With Malignant Gallbladder Diseases

Ultrasound Of The Gallbladder
Gallbladder Adenomyomatosis Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
The Gallbladder Radiology Key
Ultrasound Of The Gallbladder

Emergent Right Upper Quadrant Sonography Spence 09 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library
Ultrasound Of The Gallbladder

The Gallbladder Radiology Key
Epos
Benign Gallbladder Diseases Imaging Techniques And Tips For Differentiating With Malignant Gallbladder Diseases

Emergent Right Upper Quadrant Sonography Spence 09 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library
Benign Gallbladder Diseases Imaging Techniques And Tips For Differentiating With Malignant Gallbladder Diseases

Medpix Case Gallbladder Cholesterol Polyp
Gallbladder Adenomyomatosis Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Gallbladder Biliary Tree Pathology Flashcards Quizlet
Ultrasound Of The Gallbladder

Epos
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrzcz4mpffev61cm Vrbemfpdpmzixrllhmpk39uco Usqp Cau
The Gallbladder Radiology Key

Emergent Right Upper Quadrant Sonography Spence 09 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library

Emergent Right Upper Quadrant Sonography Spence 09 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library

An Echogenic Non Mobile Structure Attached To The Gallbladder Wall Download Scientific Diagram
Benign Gallbladder Diseases Imaging Techniques And Tips For Differentiating With Malignant Gallbladder Diseases
The Biliary System Radiology Key

Emergent Right Upper Quadrant Sonography Spence 09 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library
1

Emergent Right Upper Quadrant Sonography Spence 09 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library
Benign Gallbladder Diseases Imaging Techniques And Tips For Differentiating With Malignant Gallbladder Diseases
Diseases Of The Liver Radiology Key

Medpix Case Adenomyomatosis

Ultrasonography

A 62 Year Old Woman With Right Upper Quadrant Pain Sonography Shows Download Scientific Diagram
The Gallbladder Radiology Key
Epos

File Ultrasound Of Gallbladder Adenomyosis Jpg Wikipedia
Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 Rg
Diseases Of The Liver Radiology Key

Emergent Right Upper Quadrant Sonography Spence 09 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library

Gallbladder With Multiple Gallstones Arrows Indicate Stones With Download Scientific Diagram
Secured Societyhq Com Lars 19spring Program Lectures Lars 19spring Ca 9143 Pdf
Biliary Imaging For Gallstone Disease Springerlink
Diseases Of The Liver Radiology Key
Benign Gallbladder Diseases Imaging Techniques And Tips For Differentiating With Malignant Gallbladder Diseases
1

Transverse Plane Of The Fetal Abdomen At 24 Weeks Gestation Showing Download Scientific Diagram
Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 Radiographics 3 G00ma

Radiology Charts
Epos

Liver Gallbladder Flashcards Quizlet

Gb Cholesterolosis Multiple Echogenic Non Mobile Foci Without Posterior Shadowing Located In The Wal Ultrasound Ultrasound Sonography Medical Ultrasound
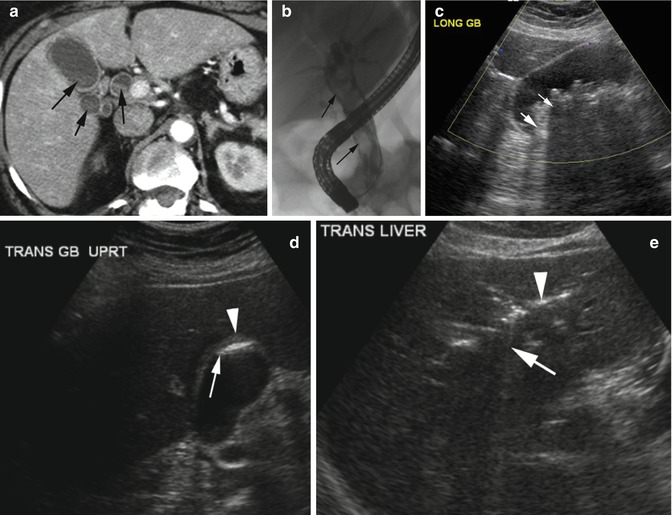
Diseases Of The Liver Radiology Key

Gallstones Html
Benign Gallbladder Diseases Imaging Techniques And Tips For Differentiating With Malignant Gallbladder Diseases
Diseases Of The Liver Radiology Key

Medpix Case Choledocholithiasis And Cholelithiasis
Gallbladder Polyp Wikipedia
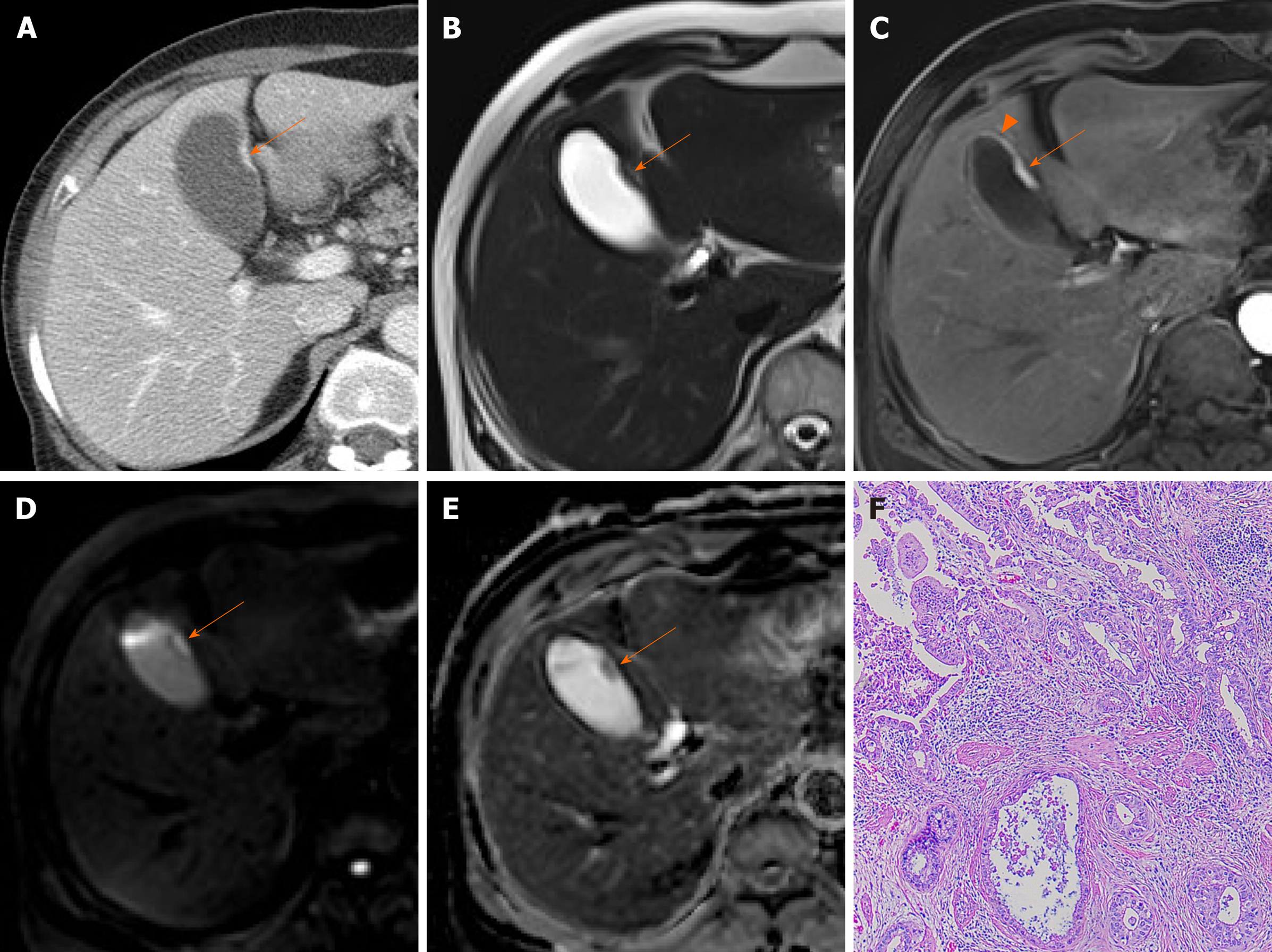
Benign Gallbladder Diseases Imaging Techniques And Tips For Differentiating With Malignant Gallbladder Diseases

Emergent Right Upper Quadrant Sonography Spence 09 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library
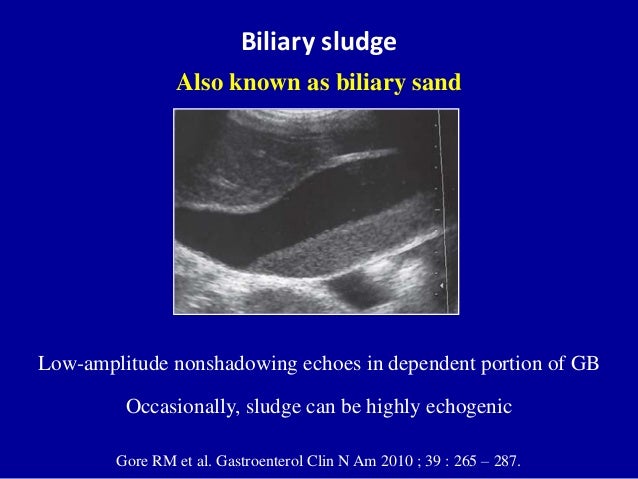
Ultrasound Of The Gallbladder

Gallbladder Stones Imaging And Intervention Radiographics
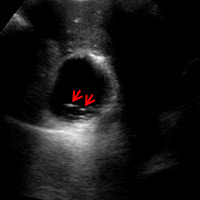
On The Case Radiology Today

An Echogenic Non Mobile Structure Attached To The Gallbladder Wall Download Scientific Diagram

Emergent Right Upper Quadrant Sonography Spence 09 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library
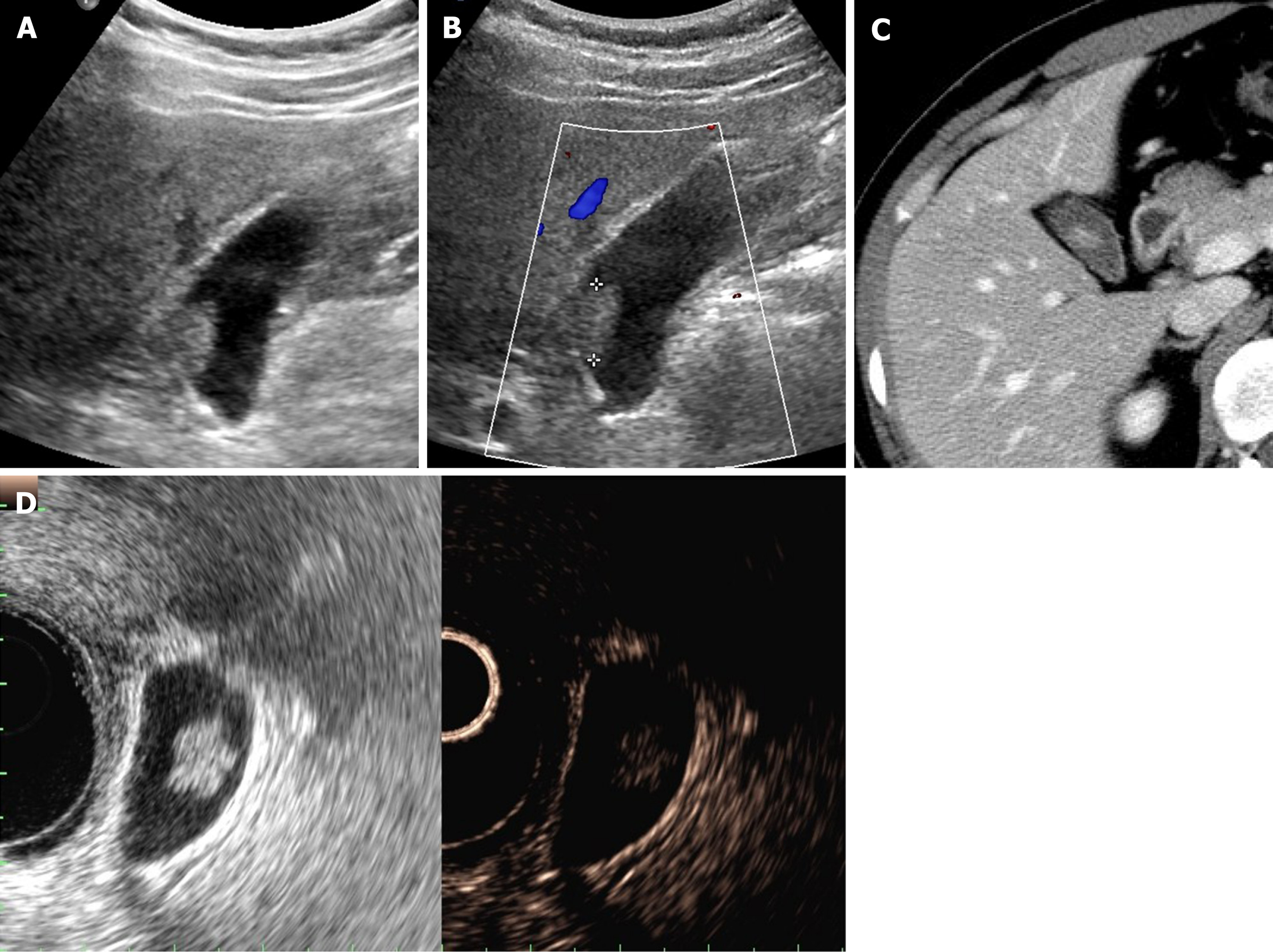
Benign Gallbladder Diseases Imaging Techniques And Tips For Differentiating With Malignant Gallbladder Diseases
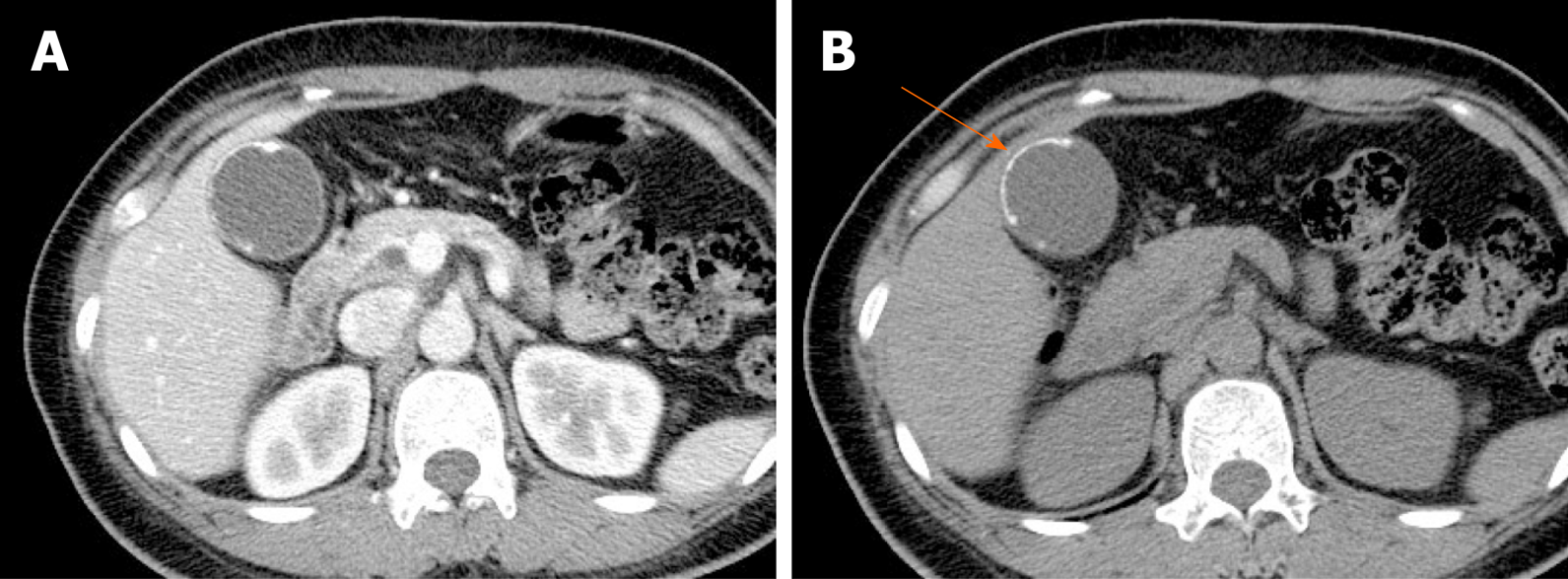
Benign Gallbladder Diseases Imaging Techniques And Tips For Differentiating With Malignant Gallbladder Diseases

Mysteries Of The Gallbladder Chamber Of Echoes The Em Pulse

Gallbladder Polyp Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
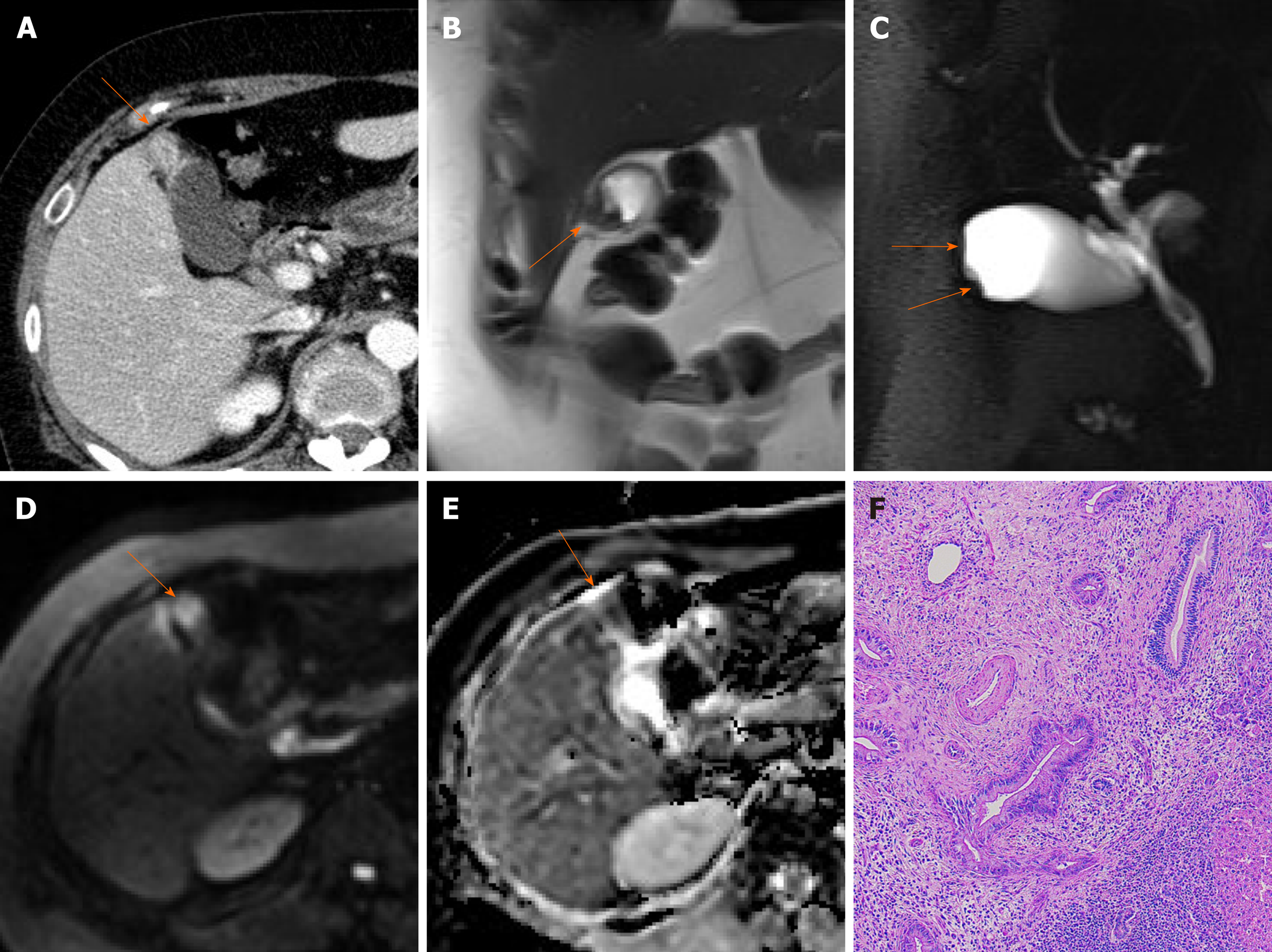
Benign Gallbladder Diseases Imaging Techniques And Tips For Differentiating With Malignant Gallbladder Diseases

Gallbladder Stones Imaging And Intervention Radiographics

Emergent Right Upper Quadrant Sonography Spence 09 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library

Gallbladder Stones Imaging And Intervention Radiographics

Ultrasound Of The Gallbladder
Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 Radiographics 3 G00ma

Ultrasonography

Missed Gallstones Or Gallbladder Clinical Gastroenterology And Hepatology

Polypoid Lesions Of The Gallbladder Disease Spectrum With Pathologic Correlation Radiographics

Radiology Charts

Ultrasound Images Gall Bladder Polyp 2 Accuvix Xq
Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 Radiographics 3 G00ma

The Effervescent Gallbladder A Rare Ultrasonographic Finding That Reflects The Presence Of Gas Within The Gallbladder Abstract Europe Pmc
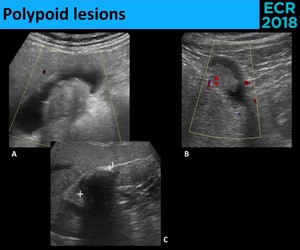
Epos

Emergent Right Upper Quadrant Sonography Spence 09 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library
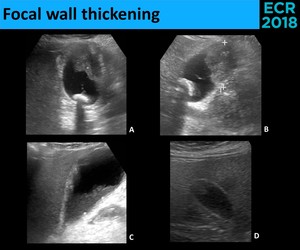
Epos
Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 Radiographics 3 G00ma

Polypoid Lesions Of The Gallbladder Disease Spectrum With Pathologic Correlation Radiographics

02 Gall Bladder Gallbladder Liver
Gallbladder Polyps Radiology Key



